Talk about an overload of information!!
To look at Google Search Google with no purpose, I can tell you from personal experience is just a chaotic and overwhelming experience! One that leaves you confused, concerned, and just really a bit stressed and at a loss.
Those are pretty much all of the things that you don’t want to be right? Well, the somewhat random assortment of search reports are useful and free to website owners.
They provide valuable insights and don’t worry, you are not alone, not all of them provide critical insights – I call those the easy on the eye reports, pretty to look at, but no real insights.
Google Search console is reliable if you are motivated enough and especially if you are on a tight budget, this tool will get you well on your way on the long journey that is SEO.
Today I am going to briefly discuss the 11 more useful Google Search Console features and show you a little ‘How To Do’, your welcome.
1. Can Google See You
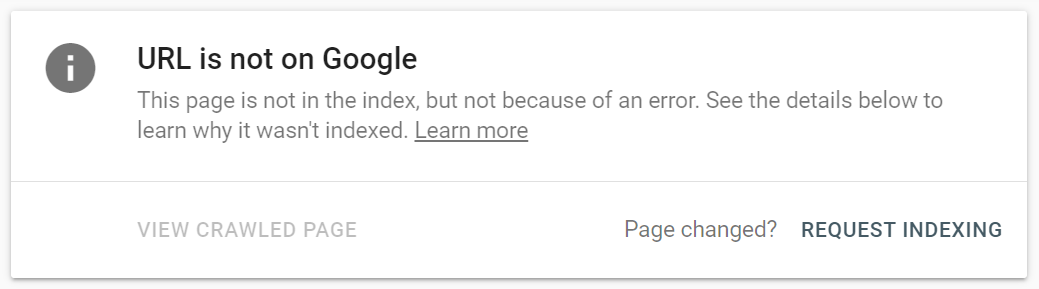
Indexing issues!! If Google can’t see you then neither can your target audience. Simple as that. Google Search Console to the rescue.
Check if Google can see all of the pages that you would like to appear in the SERP’S.
When Google is blocked from a page and this can happen accidentally, those pages are essentially just sitting ducks, bringing you no traffic whatsoever.
The Fixing of Indexing Issues
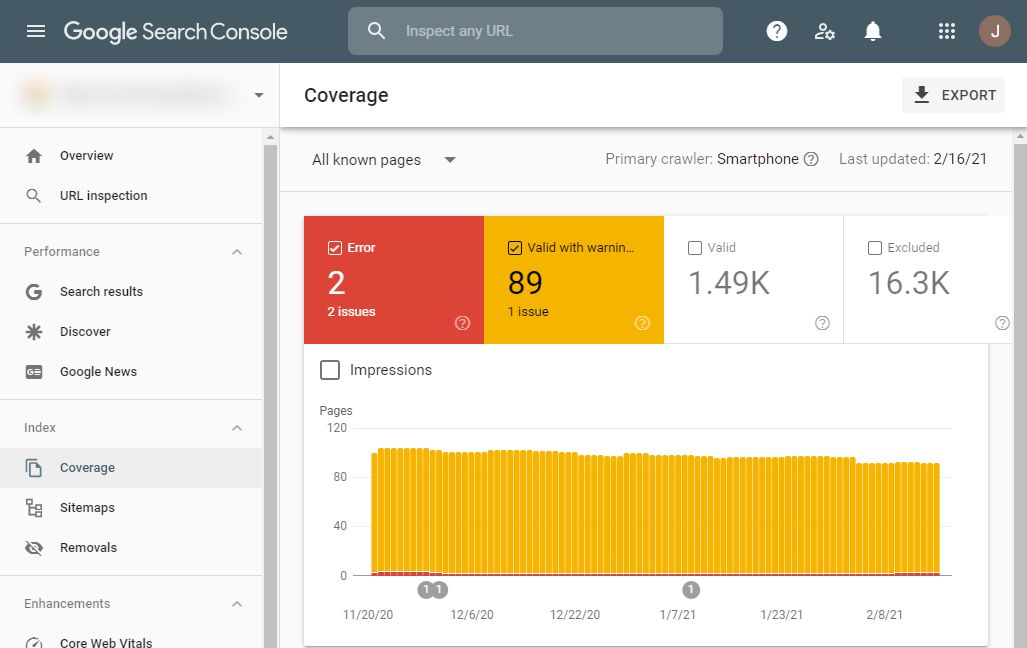
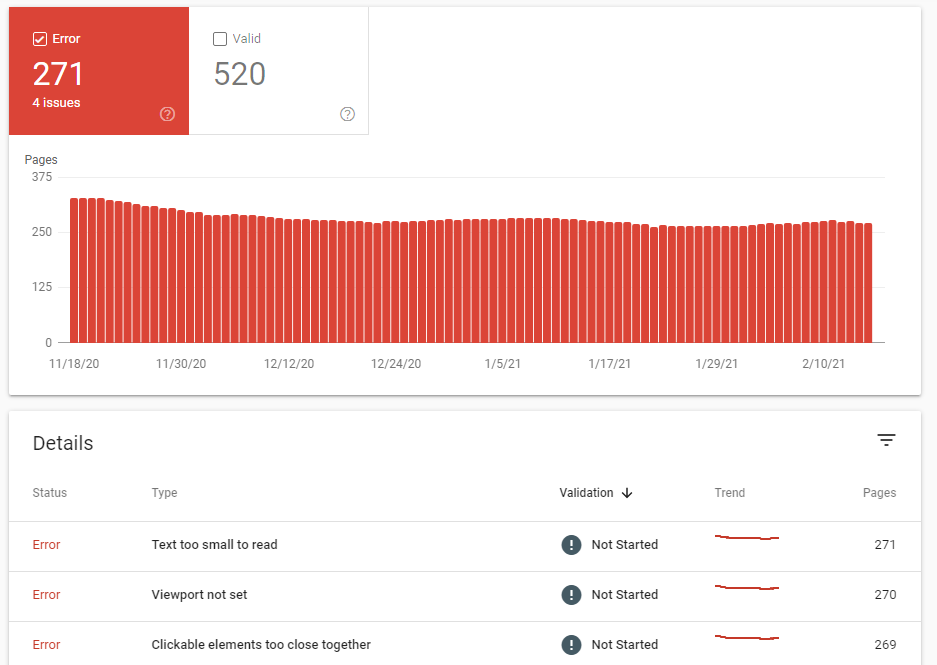
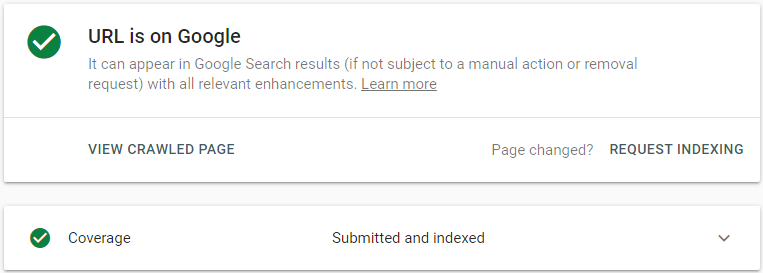
- Index> Coverage and check the status of your webpage:
Red and Yellow: Pay attention to your error messages.
-
Errors
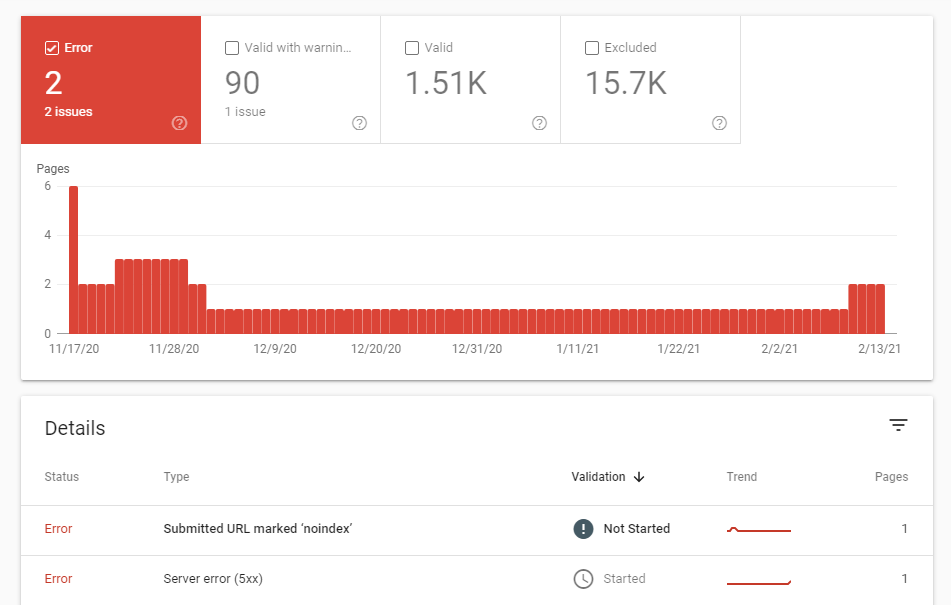
Errors are generally displayed because they either do not exist or that have restricted access.
Example Below: Submitted URL marked ‘noindex’ and Server error (5xx).
Each error is clickable and you can click on each of the errors and get a list of the URL’s that are affected.
-
Common Errors
Submitted URL cannot be indexed
This is when you have requested indexing, but Google cannot access the page. The first thing to check in this instance would be if you have requested this on purpose.
If you don’t want it indexed, just recall your request for index, most likely the reason for this is that the URL has ended up in your sitemap, just take it out.
If you do want your page indexed, you must stop blocking Google from doing its job. Of course, there are an array of ways to go about this. No matter the reason, Google any of the following and allas, you will be met with a simple resolution.
You’ll be happy, your website will be happy and Google will be happy. Win, win, win situation.
- Submitted URL marked ‘noindex’
- Submitted URL not found (404)
- Submitted URL seems to be a Soft 404.
- Submitted URL blocked by robots.txt
- Submitted URL returns unauthorized request (401)
- Submitted URL returned 403
Once you have removed the block, submit it to be indexed using your URL inspection tool.
-
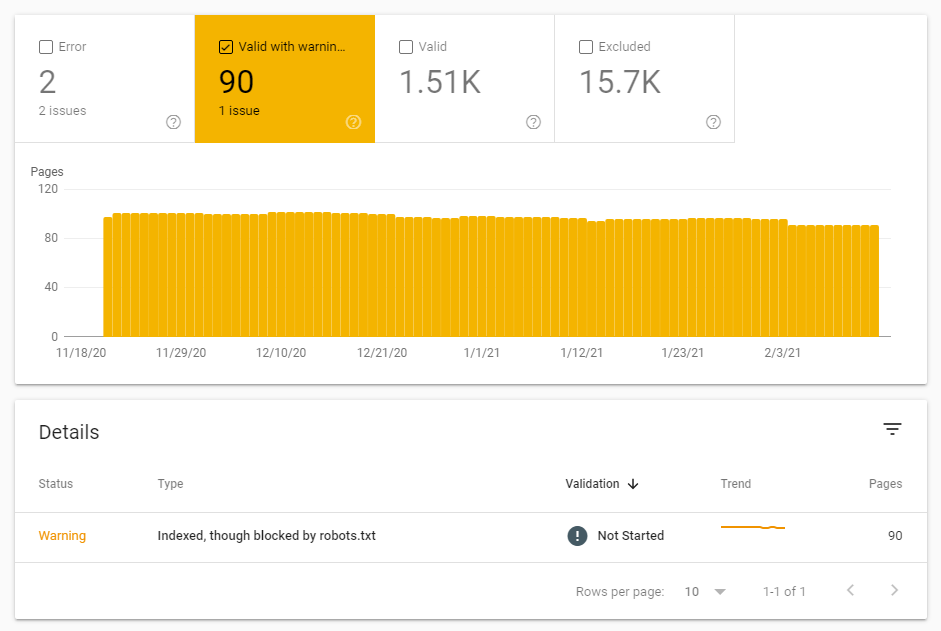
Just a little warning that Google is becoming increasingly concerned.
Google will always let you know if they have indexed something that they are not sure was meant to be.
In terms of SEO, warnings can sometimes be more alarming than errors – what if Google is showing something that is not supposed to be shown, generally shown as Indexed, though blocked by robots.txt .
How to fix this issue?
- Blocking it, then add the noindex tag to the page or remove the page : Index > Removals > New request.
Allocation of resources for technical Audits on your website, including your website’s design will show issues such as broken images, links, videos, duplicate content, meta descriptions, localisation problems and so many more – and is well worth the time and effort.
2. Optimize user experience
Web Design and functionality. This is an area that I believe personally is overlooked by a lot of businesses. Why? I don’t think that the majority of people know that you have under 8 seconds before you lose a visitor to a poor user experience.
Poor user experience (UX) = Lower levels of engagement and higher bounce rates.
Now, here’s the catch – there’s always a catch. If you think, oh I’ve just lost a few customers, then you would be wrong. When user activity declines, Google has been known to decide that based on this that your pages are less relevant – You start dropping, not good!
Again Google Search Console to the rescue, with UX reports galore, so we can get to the root of the problem and fix it before we enter the dreaded decline stage.
-
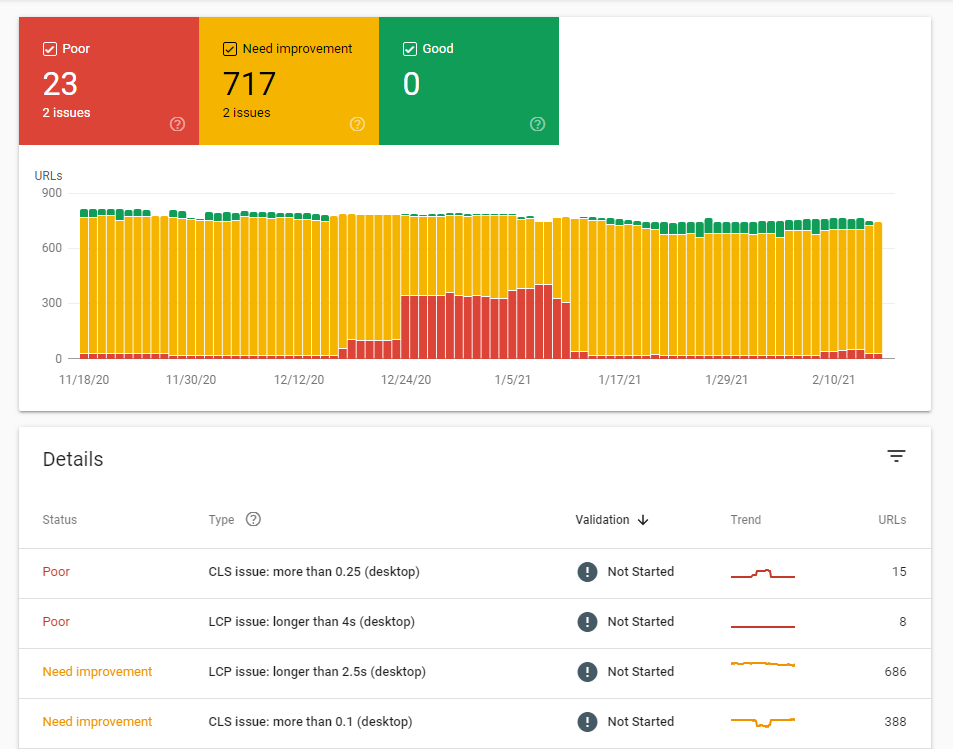
Core Web Vitals report
Judging a page in its loading stage based on:
- Speed
- Interactivity
- Visual stability
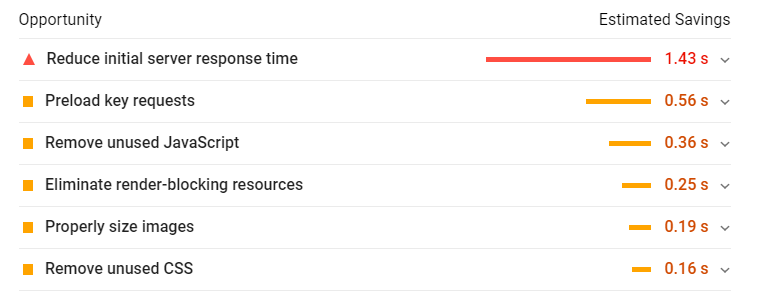
The benchmark? What are they looking for? Under 2.5 seconds is Googles standard to become interactive to the user. Now, the average speed is 18.8, Google aren’t saying it has to be 2.5, they are just pretty much saying you have to be faster than your competitors.
Once you open the Core Web Vitals report, the tool will show you how many of your pages need changes and will bring a list of issues (if there are any) to your attention.
How to Check:
- Click the issue> click on the URL > PageSpeed Insights for a more detailed report and thankfully – SOLUTIONS.
-
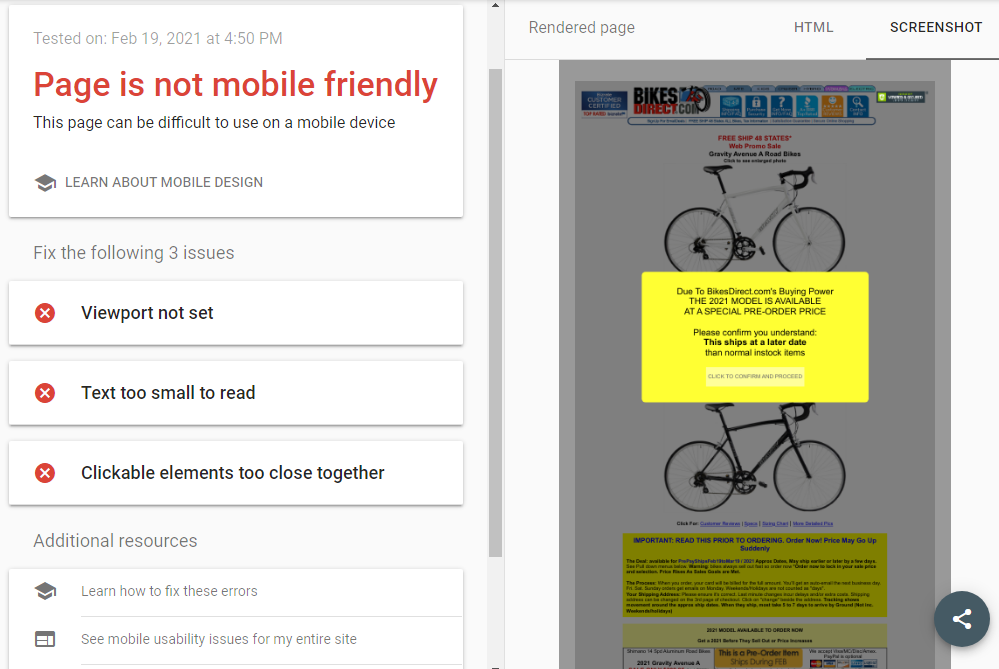
Mobile Usability report
The mobile usability report shows you the issues that mobile users experience while on your website.
The errors described, so you can understand what it is that you need to fix, and how.
Top Tip: Each issue is clickable for more insights and there is always helpful information on how to go about each issue.
Once all of the errors are fixed, click the Validate fix button to remove the error from the report.
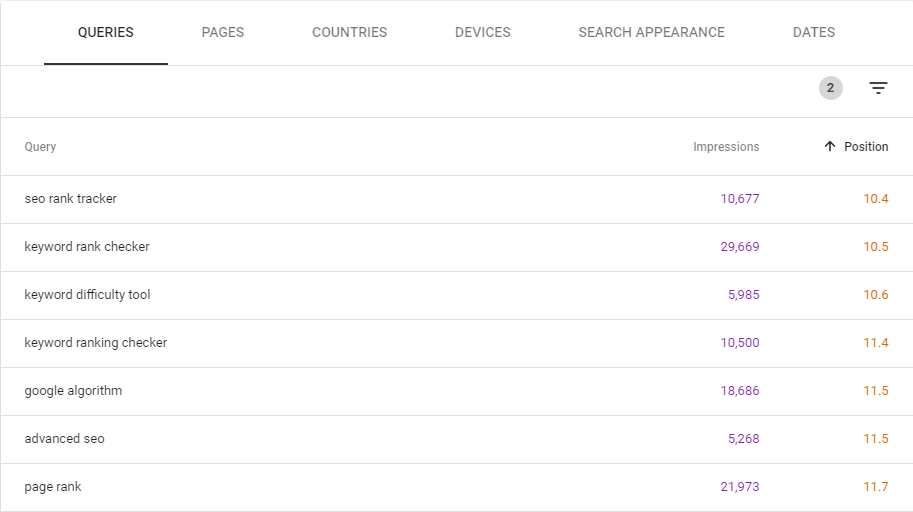
3. Are Your Keywords Underperforming
Your keywords are tracked in Google Search Console. If a keyword is on the verge of occupying big volumes of traffic, then a little optimisation on these pages will go a long way in boosting your traffic.
On the other hand, you can also find underperforming keywords:
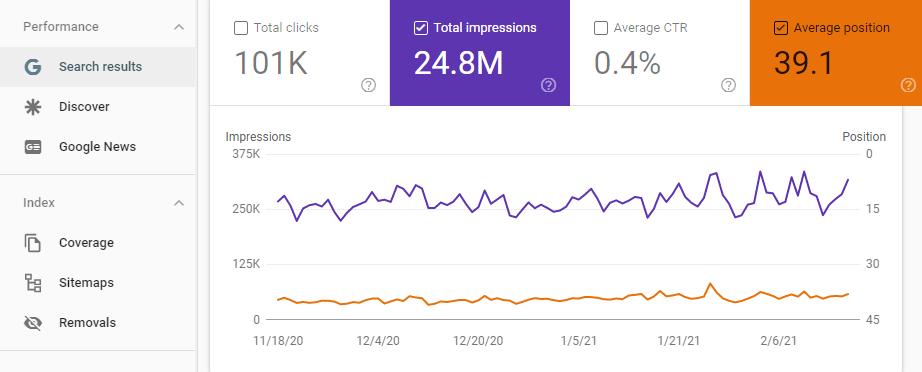
- Performance > Search results, enable Total impressions and Average position and scroll down to the table of queries.
Filter the underperforming keywords:
- Filter > position > greater than, and set the cutoff point depending on your strategy (Impressions/Rank etc)
If a keyword is currently in position 5, but gets 20 impressions per month, there is little to be gained from moving this keyword to a better position. Click filter > impressions > greater than to eliminate keywords with very low impression count.
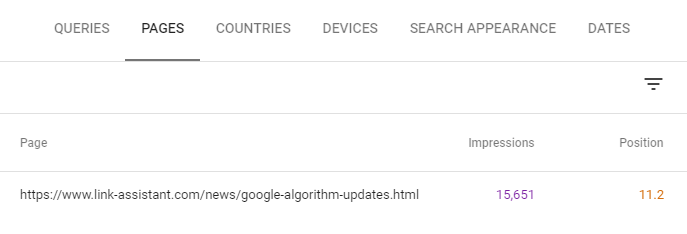
When you have your list of underperforming keywords you can then click a certain query and select Pages to see the pages that rank for the query.
4. Find Underperforming Snippets
Google Search Console is a useful tool to figure out if some of your snippets have a lower Click Through Rate than is normal for their position.
Each position in search results averages a certain percentage of clicks. For example, if you rank in position one, your CTR is likely to be around 30%. If it’s significantly below 30%, then there might be something wrong with your snippet.
How To Do It:
- Performance > Search results, enable Average CTR, Average position, and Total impressions.
Filter impressions to eliminate low-quantity keywords, and sort the table by Position in ascending order:
Pay attention to the CTR’s that seem too low and investigate. Type the underperforming query into Google. There are a few reasons that could result in a low click through rate:
- SERP’s might contain a lot of ads or featured snippets that take most of the users’ attention and clicks
- Your snippet is not as catchy as those of your competitors.
As always, there are so many tools to help with this, find out what your competitors are doing and do that.
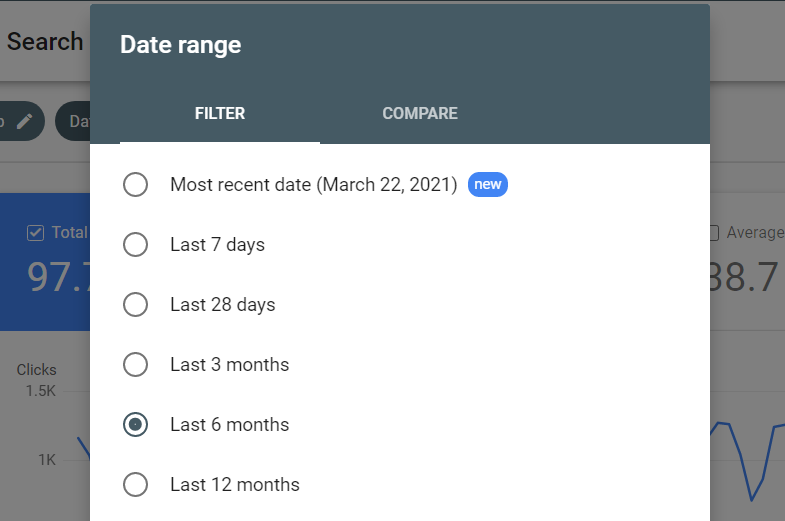
5. Do Your Pages Need An Update?
Google Search Console’s Search results feature shows you what pages need a bit of a revamp.
Now don’t worry about a page being flagged for this, it is 100% natural for this to happen, just a little bit of TLC and you’ll be back.
How To Do It:
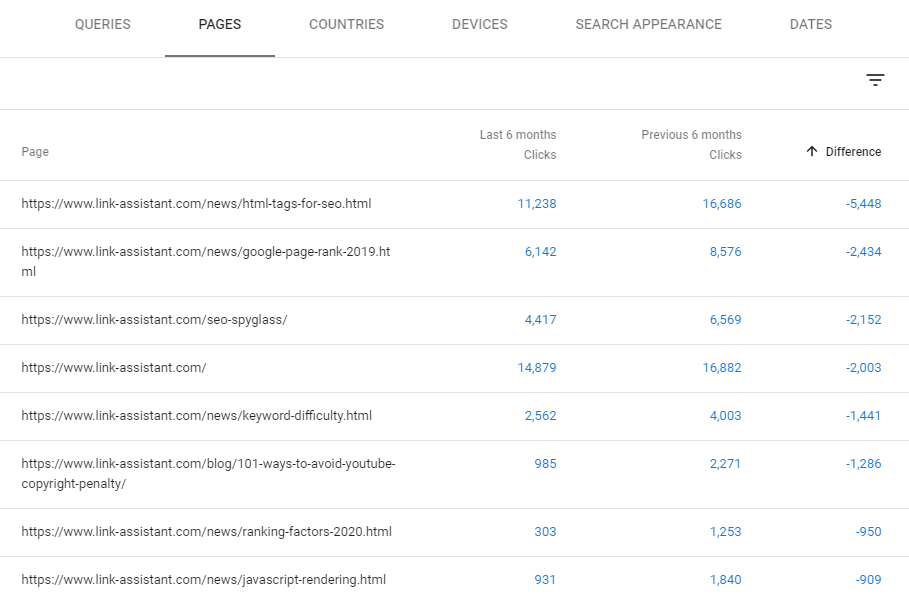
- Date > Compare > Compare last 6 months to previous period
- Enable Clicks, and switch to Pages to see what pages experienced the greatest traffic loss over the last six months.
Look through the page that says it needs an update and check to see if the information is still relevant and make sure to compare it to the competitors’ pages on the same topic. Are there enough keywords? Are titles okay? Are they optimised?
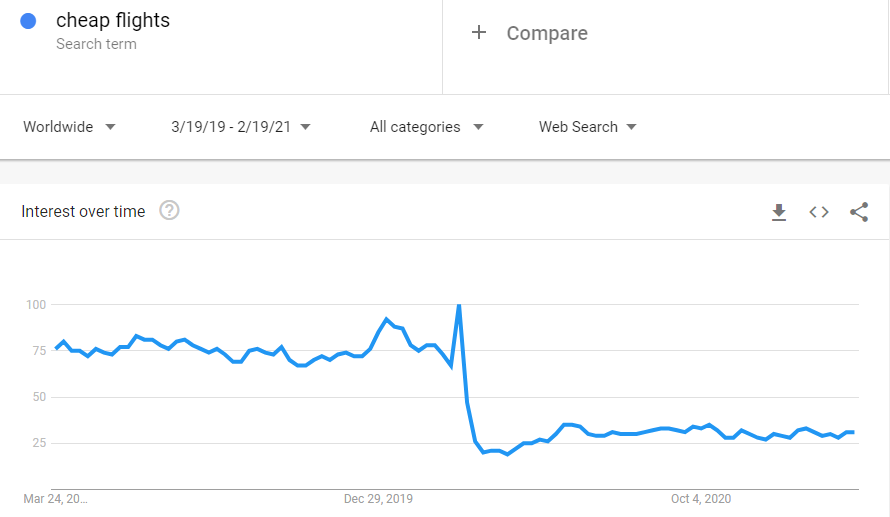
Sometimes it is not that the information is up to date, sometimes it is genuinely not relevant anymore, take Covid 19 as a prime example of this. Cheap flights were no longer relevant sadly, very sadly, and so they plummeted.
6. Backlinks
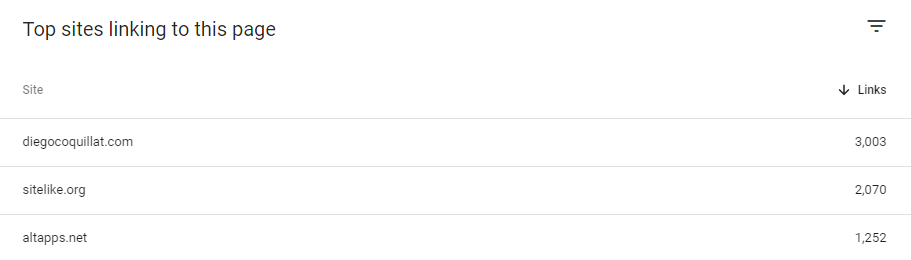
Backlinks are important in terms of ranking factors. GSC of course can tell you how many backlinks that you have.
Check how many backlinks you have, and what websites link to you.
How To:
- Click links on the left side menu > Click more on the Top linked pages table in the External links section.
Sort linking sites, and click on a line to see what domains link to your page. The truth with GSC is that the backlink report lacks information for you to carry out a proper evaluation on the quality of backlinks and you will need to use another software. It is good at a glance, just to keep an eye on things while your in and checking out everything else.
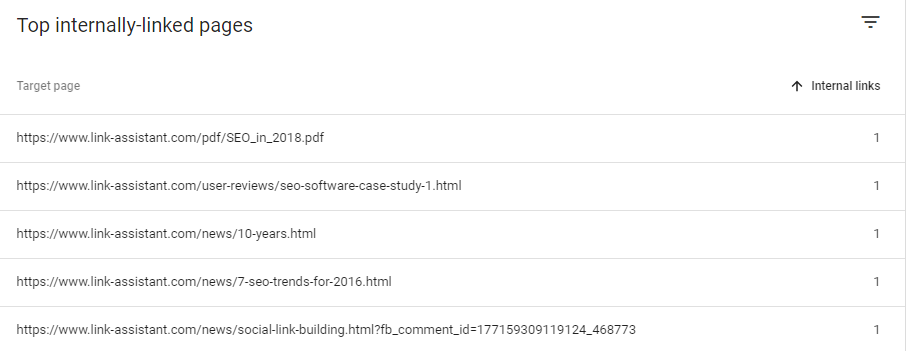
7. Opportunities For Internal Linking
My previous article on internal links will give you an overview of what internal links are and explore them more in depth if you wish to have a look into the wonderful realm of internal linking, be my guest.
Internal links are most definitely a ranking factor, although arguably one of the less powerful, still very much important.
See which pages of yours are lacking in linking and where you need to focus your attention first.
How To:
- Top linked pages on the Internal links report. Sort the links in ascending order.
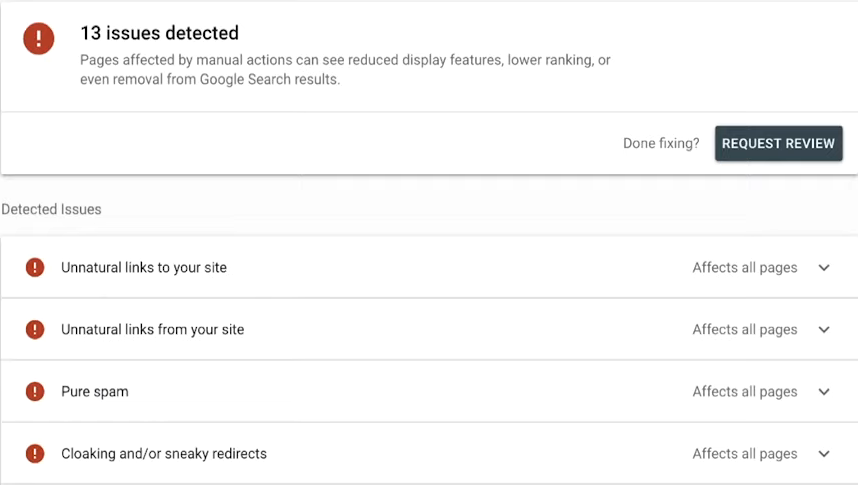
8. Manual Actions And Security Issues
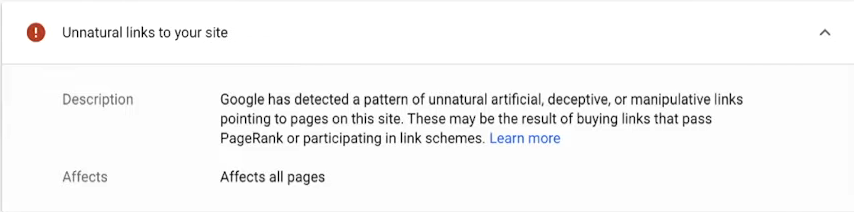
Are you compliant with Google’s Webmaster quality guidelines? Human’s- your users can submit a manual action against a website if they think that it is slipping below the bar.
What are the reasons that this might happen?
- Spam
- Black Hat SEO
- Unnatural Backlinks
- Thin Content
And as usual, so many more wonderful reasons and things that you must pay attention to. You can see a full list of malicious actions on Google. The key is to fill your site with valuable content that is helpful and useful to the consumer.
If this is something that you don’t have time for, I really do recommend using social media management services, as Google really does not like thin content and it will have an impact on you and your ranking.
Manual penalties can result in some of all of your pages being deindexed for search. This can be a reason behind a sudden loss of traffic.
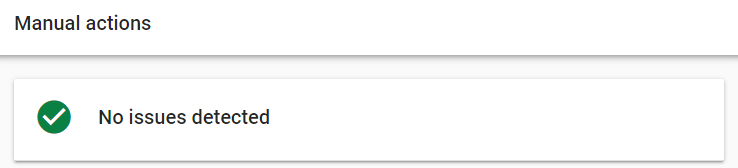
How to check:
Manual action in GSC;
If there are issues, these do need immediate attention, as always, just click on the issue and there will be a handy resolution for you. To get back on track.
This is an issue that you need to fix all of to be out of the red and back into the clear, Google takes this very seriously.
Once you’ve fixed all the issues, click Request review, and describe what has been done.
- Explains the exact quality issue you had on your website
- Describe the steps you took to fix the issue
- Document the outcome of what you’ve done
Google will follow this up, with an acceptance or a denial, so don’t send another request until the previous one is answered — it will not speed up the process.
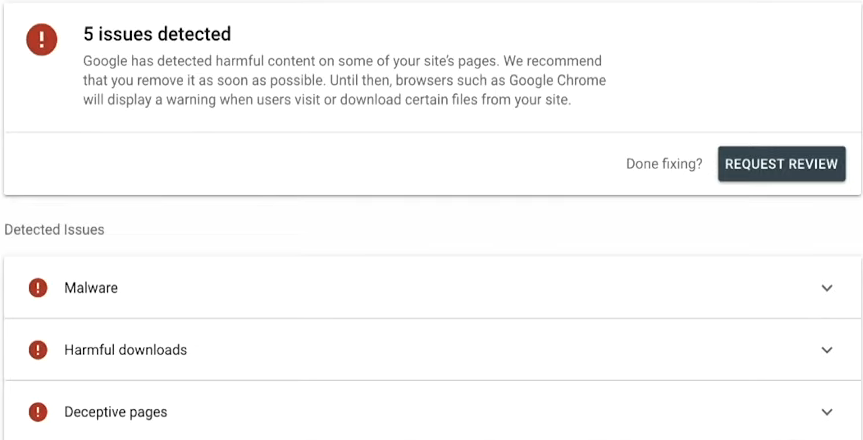
Security issues
If your website is hacked, or could potentially harm a user by phishing attacks or installing malware on a user’s computer, you will be security alerted.
The pages with security issues may appear in search with a warning label.
The algorithm is the same as for manual action issues and therefore the process.
How To Do It:
- Click into the Security issues report section of Search Console, investigate the issue, fix all of them, and request a review.
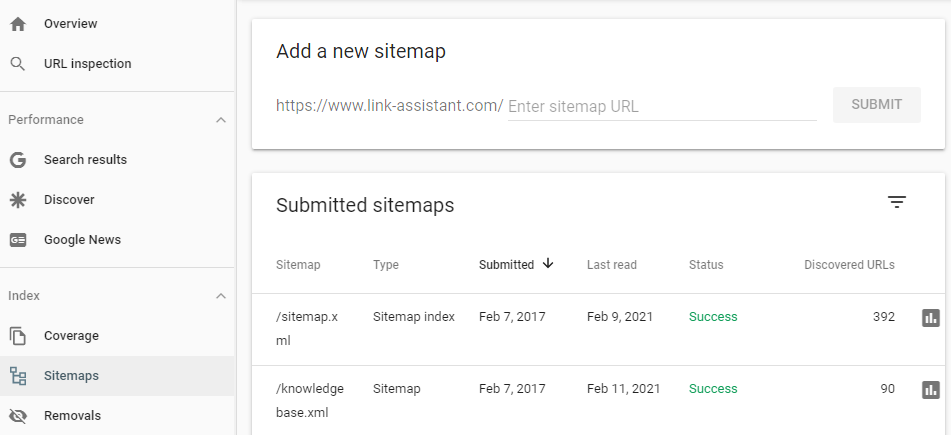
10. Add Your Sitemap
Sitemaps are something that you are probably aware of. If not, put simply, sitemaps are something put in place that helps Google to navigate the structure of your website.
What it does is:
- Where they are located
- How often they should be crawled
Essentially a sitemap is the best friend of linking. It makes the speed at which things are indexed so much faster and easier as they make it easier for Google to find pages.
If you haven’t submitted your website with GSC, then go and do it, it is definitely worth it.
How To Do It:
- Sitemaps > enter a sitemap URL > click Submit.
A sitemap file:
- must not be larger than 50 MB
- must not contain more than 50,000 URLs
If you have more than this amount of URL’s, simply add several sitemaps. In this instance, you need to list each file as a sitemap index file (always explained in there)
If there is no sitemap, then Google is left to its own devices and will crawl your site how it thinks it should, not how you would like it to. Google does not follow this strictly, but it is best practice.
11. Send New And Updated Pages For Indexing
If you have a new page or have updated a page, don’t hold off on Google coming along on its own accord and finding it. If it is ready to go, request indexing and it will appear in the search results faster.
How To Do It:
- Enter the URL into the GSC search field, and click Request indexing.
Although it may actually take anywhere between a few minutes and a few days. Still, probably faster than simply waiting.
Final thoughts
Google Search Console is a tool that is very useful to you and your online practices, it helps to not only keep track of your data but provides you with a list of priorities in order of importance. This tool, used alongside all of the others that are widely available will drive you through the obstacles that fill the SEO journey and drive traffic to your website.
About the author:
We are also experts in getting targeted traffic to your site, so not only does your website look and function great, but with our SEO plans you will have a steady supply of potential customers finding your site via organic search. We pride ourselves on ‘outcaring’ the competition by building meaningful connections with your audience through SEO. This way you’ll get the best ROI.